Gaps in Globular Cluster Stellar Streams as Probes for Dark Matter in M31 and Other Galaxies
Cosmological simulations that include dark matter predict the existence of low-mass subhalos. These subhalos can perturb thin stellar streams formed by tidal disruption of globular clusters, creating a gap-like feature like those detected in Gaia data (e.g. GD-1). In Aganze et al. 2023, we predict that the Nancy Grace Roman Telescope should be able to detect these gaps in galaxies within 3 Mpc with resolved stars. This research is done in collaboration primarily with Dr. Sarah Pearson and Dr. Tjitske Starkenburg.
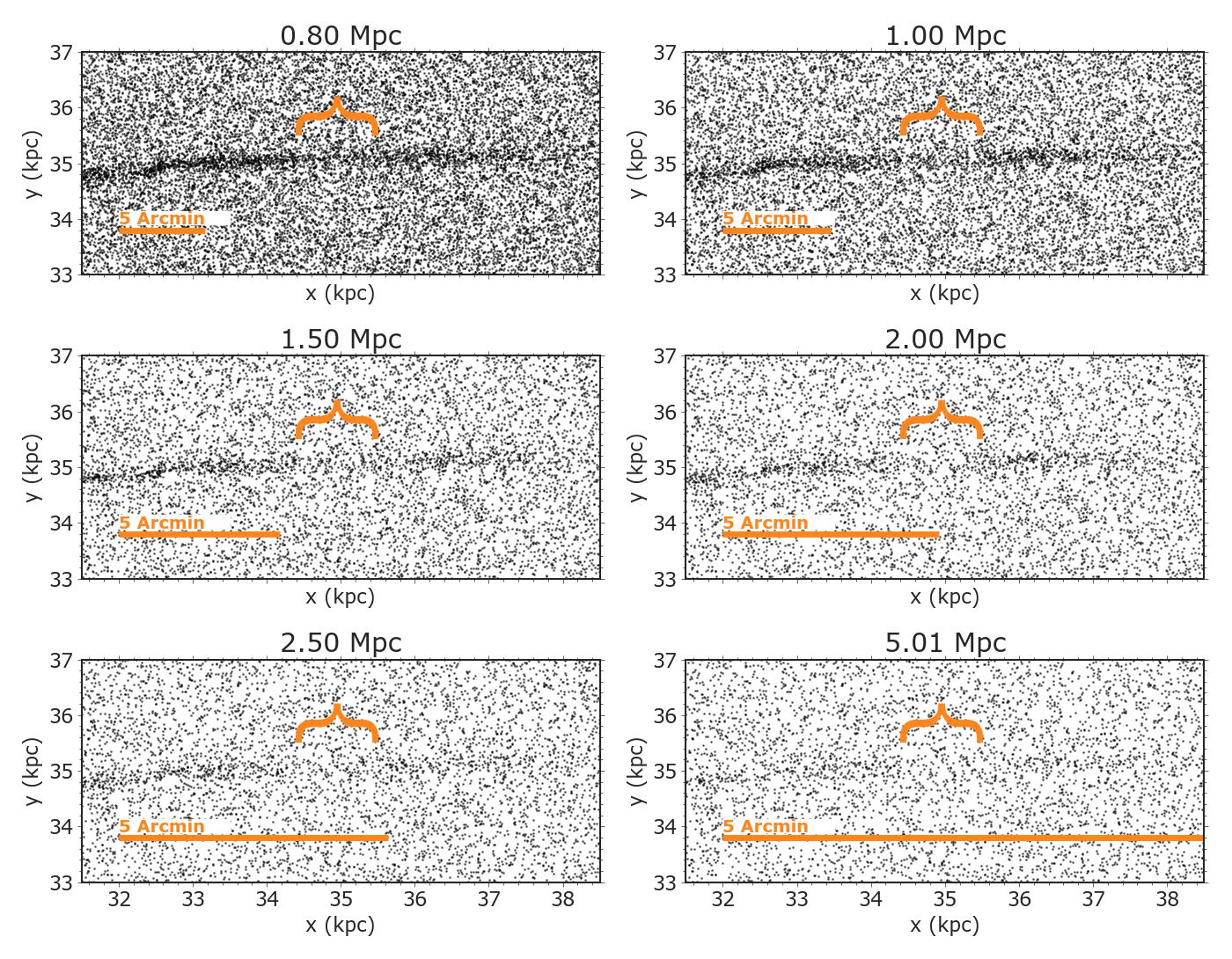 A simulation of a mock image of a metal-poor GC stream in an external galaxy for 1-hour exposure with Roman with resolved stars. The gap from a dark matter subhalo of $\approx 5 \times 10^6$ solar masses is show at the center.
A simulation of a mock image of a metal-poor GC stream in an external galaxy for 1-hour exposure with Roman with resolved stars. The gap from a dark matter subhalo of $\approx 5 \times 10^6$ solar masses is show at the center.
Galactic Archeology with Brown Dwarfs at Large Distances
Finding Brown Dwarfs and Low-mass Stars in Deep HST Parallel Fields with Machine Learning
In Aganze et al. 2022a, we used traditional index-selection methods, and machine learning techniques (random forests and neural networks) to isolate a sample of 164 M7-T9 ultracool dwarfs up to distances of ~2~kpc in the Galaxy. Similar surveys with JWST (such as the PASSAGES survey) will uncover a comparable number of objects in the galactic thick disk and halo.
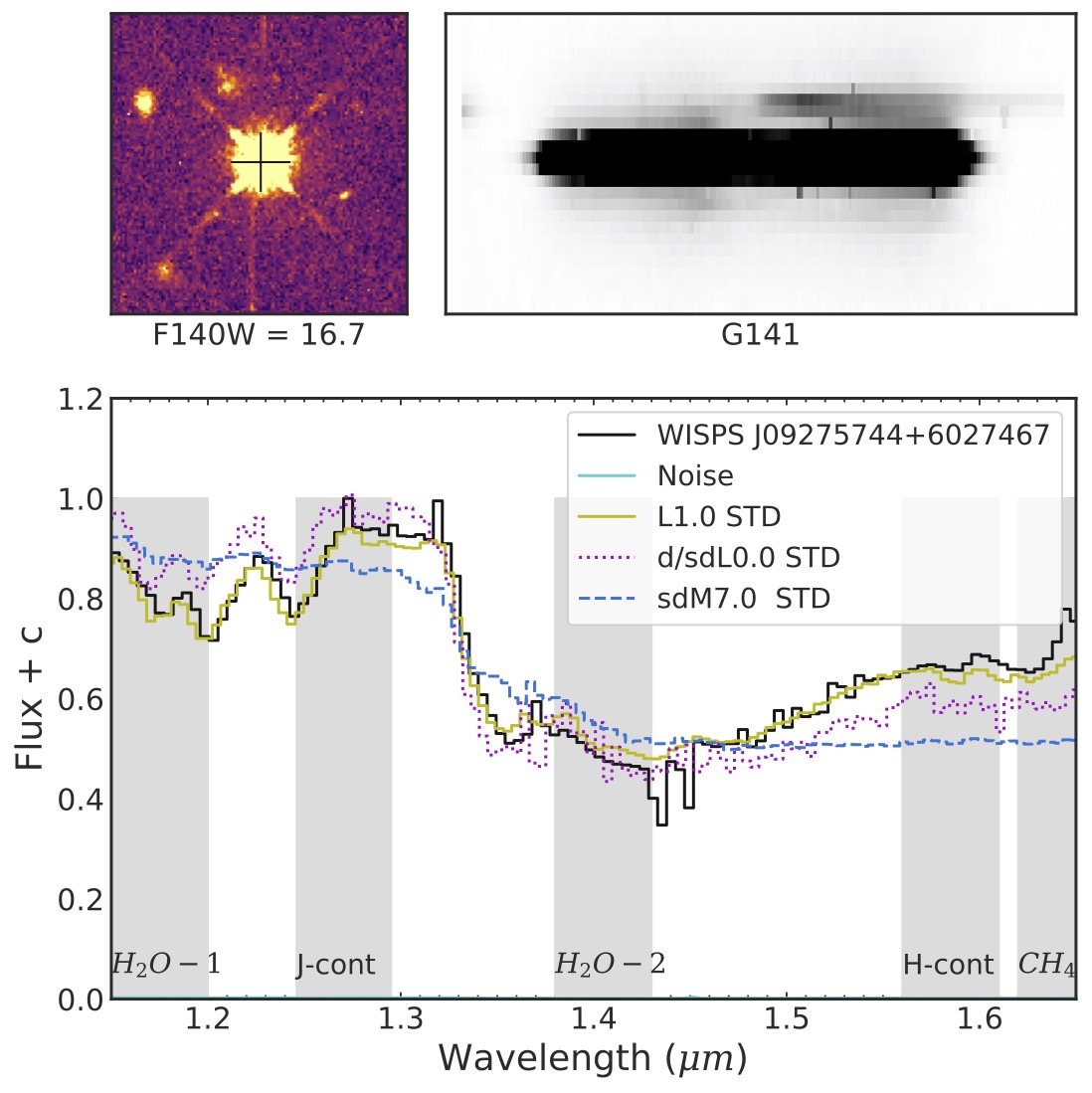
Top Left: Cutout from a processed image of an L dwarf in the WISP survey with the F140W filter (1.4 µm). Top Right: a 2D G141 (1.1-1.7 µm) spectrum of the same pointing. Bottom: 1D- Spectrum fitted to best-match spectral templates of dwarfs and metal-poor subdwarfs.
Links:
- Link to CoolStars Poster: Finding Ultracool Dwarfs in Deep HST-WFC3 Surveys with Machine Learning
- ADS Link to Paper
Scaleheights and Ages Brown Dwarfs and Low-Mass Stars in Deep HST Parallel Fields
In Aganze et al. 2022b, we used the sample from Aganze et al. 2022a to constrain the scaleheight and ages using a simulation that takes into account the stellar mass function, multiplicity, UCD evolutionary models, galactic structure and survey selection function. We found that late-M dwarfs are generally older than L and T dwarfs as expected from cooling models, with median ages ranging from 3.6-2.4 Gyr.
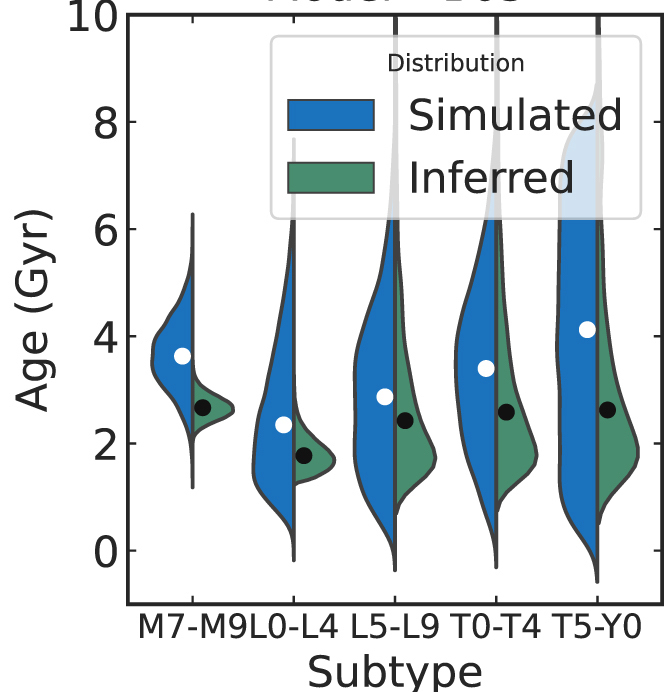
Figure from the paper showing the simulated age (blue) vs inferred age (green) of UCD sub-populations. Dots show the median age of a population.
Local M Dwarfs
Metal Poor GJ 660.1AB System
I’m also interested in the study of nearby UCDs. GJ 660.1AB is a binary system (M1 and M7 secondary) previously overlooked; in Aganze et al. 2016, we showed that the peculiarities in the spectrum of the secondary can be explained by its low metallicity.
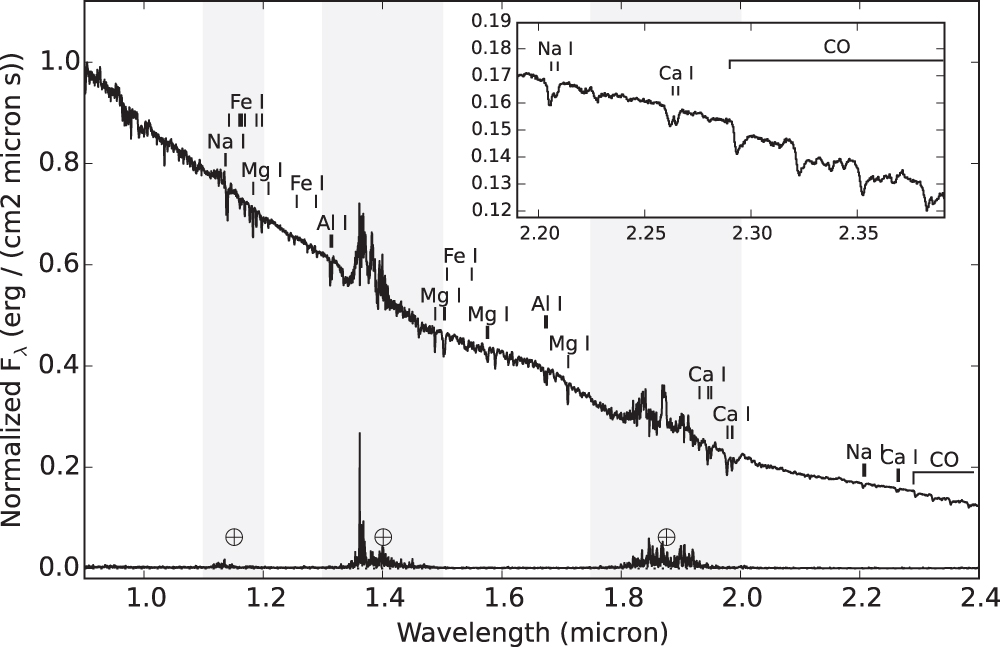
Moderate resolution SpeX SXD spectrum of the primary showing prominent atomic and molecular features in its atmosphere
Machine Learning Projects
I have mentored UCSD undergraduate students on summer projects that involve using supervised learning techniques (random forests and neural networks) to classify brown dwarfs and to identify rare populations (binaries, subdwarfs).
Links:
- Gong et al. 2022: Color Classification with SDSS, UKIDSS, and WISE Photometry
- Gutierrez et al. 2022: Color Classification with PanSTARRS, 2MASS, UKIDSS, and WISE
- Desai et al. 2023: classifying spectral binaries with machine learning